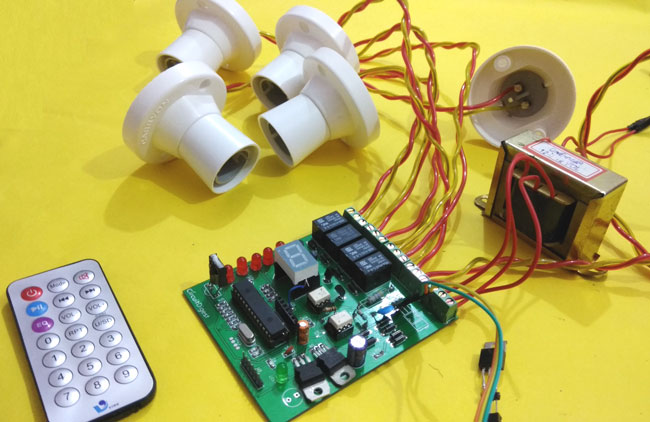
In this project, we are going to use a PIC microcontroller to remotely control few AC loads by just using an IR remote. A similar project
IR remote controlled Home automation has already been done with Arduino also, but here we designed it on PCB using
EasyEDA’s online PCB designer and simulator, and used their PCB designing services to order the PCB boards as shown in the subsequent section of the article.
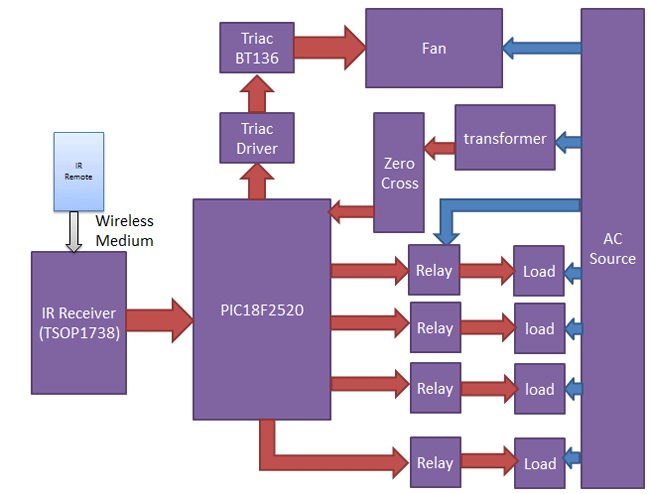
At the end of this project you will be able to toggle (ON/OFF) any AC load using an ordinary Remote from the comfort of your Chair/Bed. To make this project more interesting we have also enabled a feature to control the speed of the fan with the help of Triac. All these can be done with simple clicks on your IR remote. You can use any of your TV/DVD/MP3 remote for this project. The different IR signals from the remote are received by the microcontroller which then controls the respective relays via a relay driver circuit. These relays are used to connect and disconnect the AC Loads (Lights/Fan).
Working Explanation:
The working of this project is fairly simple to understand. When a button is pressed on the IR Remote it sends a sequence of code in form of encoded pulses using 38Khz modulating frequency. These pulses are received by the TSOP1738 sensor and then read by the Controller. The Controller then decodes the received train of the pulses into a hex value and compares it with the predefined hex values in our program.
If any match occurs then the controller performs a relative operation by triggering the respective Relay/Triac and the corresponding result is also indicated by on-board LEDs. Here in this project, we have used 4 bulbs (small bulbs) of different colors as lighting loads and another bulb (bigger bulb) is considered to be a fan for demonstration purpose.
We have selected key 1 to toggle the relay1, 2 to toggle the relay2, 3 to toggle the relay3, 4 to toggle the relay4, and Vol+ to increase fan speed and Vol- to decrease speed of the fan.
Note: Here we have used 100watt bulb instead of a fan.
There are many types of IR Remotes available for different devices, but most of them work around 38KHz Frequency. Here in this project, we control home appliances using IR TV remote and for detecting the IR signals, we use a TSOP1738 IR Receiver. This TSOP1738 sensor can sense 38Khz Frequency signal. The working of IR remote and the TSOP1738 is covered in detail in this article:
IR Transmitter and Receiver
Our PIC microcontroller operates at +5V and the Relays operate at +12V, Hence we use a transformer to step down the 220V AC and rectify it using a full bridge rectifier. This rectified DC voltage is then regulated to +12V and +5V by using the regulator ICs 7812 and 7805 respectively.
To trigger the relay we make use of transistors like BC547 which can act as an electronic switch to turn ON/OFF the relays based on the signal from the PIC microcontroller.Further to control the speed of the fan we are using a TRIAC. TRIAC is a power semiconductor which is capable of controlling the output voltage; this capability is used to control the speed of the fan.
We have also used a Triac Driver to control the Triac using our PIC microcontroller. This driver is used to give a firing angle pulse to Triac, so that the output power can be controlled. Here we have used 6 level of speed control. When the level is 0 then the fan will be off. When level will be 1 then speed will be 1/5th of full speed. When level will be 2 then speed will be 2/5th of full speed and respectively for others. The current level of the speed can be monitored using the on-board
7-segment display.
The block diagram of the project is shown below.
Components:
The components required to build this project is given below:
- PIC18f2520 Microcontroller -1
- TSOP1738 -1
- IR TV/DVD Remote -1
- Transistor BC547 -4
- Relays 12 volt -4
- Bulb with holder -5
- Connecting wires -
- EasyEda PCB -1
- 16x2 LCD
- Power supply 12v
- Terminal connector 2 pin ` -8
- Terminal Connector 3 pin -1
- Transformer 12-0-12 -1 -
- Voltage Regulator 7805 -1
- Voltage Regulator 7812 -1
- Capacitor 1000uf -1
- Capacitor 10uf -1
- Capacitor 0.1uf -1
- Capacitor 0.01uf 400V ` -1
- 10k -5
- 1k -5
- 100ohm -7
- Common cathode segment -1
- 1n4007 diode -10
- BT136 triac -1
- Male/female header -
- LEDs -6
- Opto-coupler moc3021 -1
- Opto-coupler mtc2e or 4n35 -1
- 20Mhz crystal -1
- 33pf capacitor -2
- 5.1v zener diode -1
- 47 ohm 2 watt resistor -1
All these components are commonly used and can be easily purchased. However if you are looking for a best buy online then we would recommend you
LCSC.
LCSC is a great online store to buy your electronics components for all kinds of projects. They feature about 25,000 kinds of components and the best thing is that they sell even small quantity items for small projects and they also have Global Shipping.
Decoding the IR Remote:
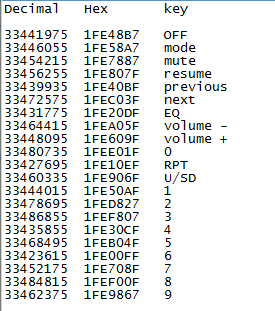
As said earlier you can use any kind remote for your project. But we have to know what kind of signal is generated for from that particular remote. For every individual key on the remote there will be an equivalent HEX value for that key. Using this HEX value we can distinguish between each key on our microcontroller side. So before we decide to use a remote we should know the HEX value for the keys preset in that particular remote. In this project, we have used a NEC remote. The HEX values for the keys on a NEC remote is given below.
As you can notice the HEX value has 7 characters out of which only the last two differs, hence we can consider only the last two digits to distinguish between each keys.
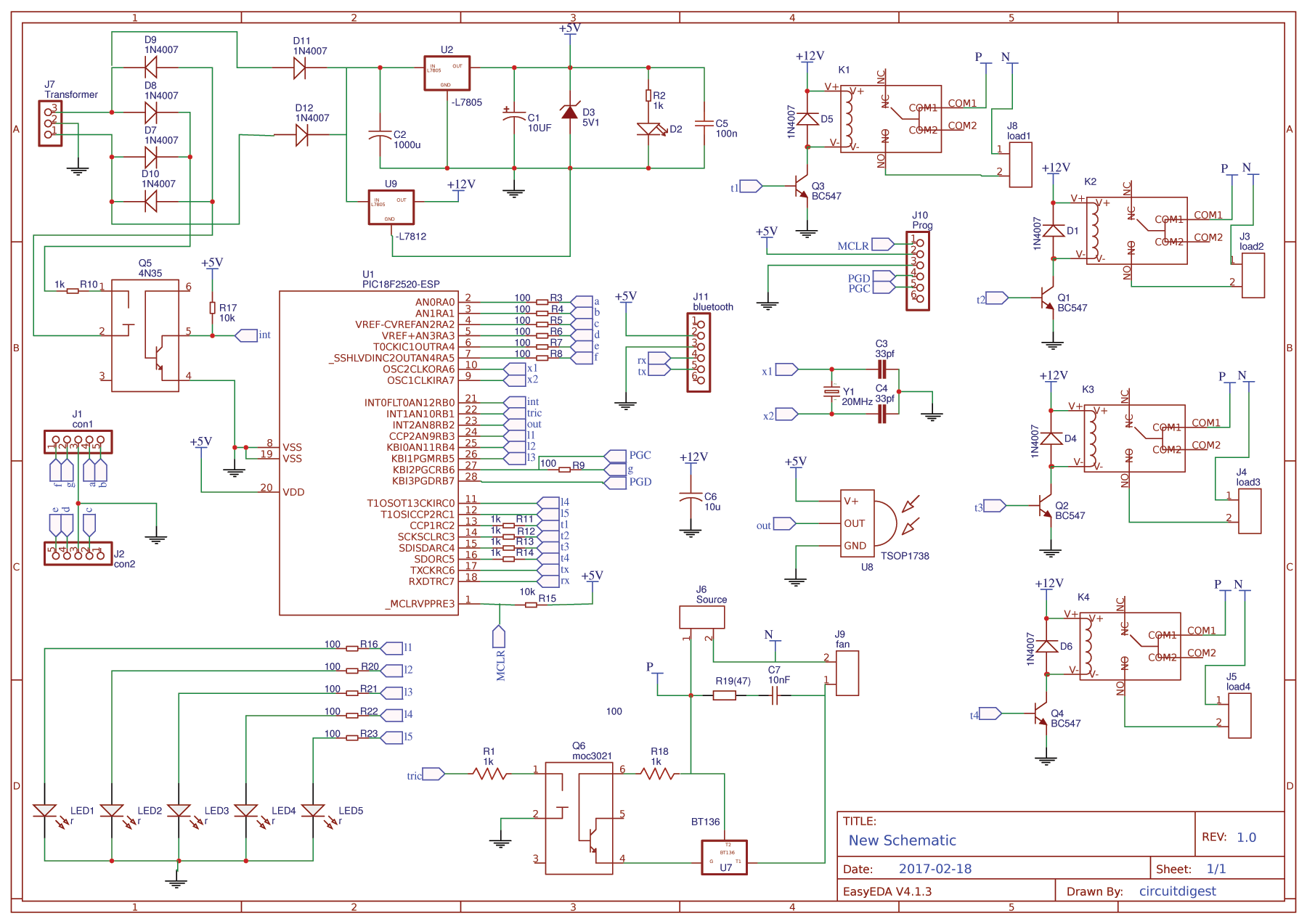
Circuit Diagram:
The schematic for the project is shown below.
The above schematic was made easy by using
esayEDA schematic editor since they provide the layouts of all components used in this project. It also does not require an installation and can be used online on the go.
The pinouts and component values are clearly specified in the schematic above. You can also download the schematic file from
here.
Programming:
The program for this project is done using MPLABX, the code is also pretty simple and easy to understand. The complete code will be given at the end of this tutorial, further few important chunks of the program are explained below.
In the beginning of the code, we should include required libraries, define the pins and declare the variables.
#include <xc.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include "config.h"
#define tric RB1
#define ir RB2
#define relay1 RC2
#define relay2 RC3
#define relay3 RC4
#define relay4 RC5
#define rly1LED RB3
#define rly2LED RB4
#define rly3LED RB5
#define rly4LED RC1
#define fanLED RC0
int flag=0;
int cmd=0;
int speed=5;
unsigned int dat[100];
int i=0;
char result[10];
int j=0;
After that, we have created a simple delay function by using the “for” loop.
void delay(int time)
{
for(int i=0;i<time;i++)
for(int j=0;j<800;j++);
}
After that, we have initialized the timer by using the following function
void timer() // 10 -> 1us
{
T0PS0=0;
T0PS1=0;
T0PS2=0;
PSA=0; //Timer Clock Source is from Prescaler
T0CS=0; //Prescaler gets clock from FCPU (5MHz)
T08BIT=0; //16 BIT MODE
TMR0IE=1; //Enable TIMER0 Interrupt
PEIE=1; //Enable Peripheral Interrupt
GIE=1; //Enable INTs globally
TMR0ON=1; //Now start the timer!
}
Now in the main function, we have give directions to the selected pins and initialize timer and external interrupt int0 to detect zero crossing.
ADCON1=0b00001111;
TRISB1=0;
TRISB2=1;
TRISB3=0;
TRISB4=0;
TRISB5=0;
TRISC=0x00;
TRISA=0x00;
PORTA=0xc0;
TRISB6=0;
RB6=1;
relay1=0;
relay2=0;
relay3=0;
relay4=0;
rly1LED=0;
rly3LED=0;
rly2LED=0;
rly4LED=0;
fanLED=0;
i=0;
ir=0;
tric=0;
timer();
INTEDG0 = 0; // Interrupt on falling edge
INT0IE = 1; // Enable the INT0 external interrupt (RB0)
INT0IF = 0; // Clears INT0 External Interrupt Flag bit
PEIE=1; //Enable Peripheral Interrupt
GIE=1; //Enable INTs globally
Now, here we are not using any interrupt or capture and compare mode to detect IR signal. Here we have just used a digital pin to read data just like we read a push button. Whenever signal goes high or low we just put debouncing method and run the timer. Whenever pin changes its state to another then time values will be saved in an array.
IR remote send logic 0 as 562.5us and logic 1 as 2250us. Whenever timer reads around 562.5us then we assume it 0 and when timer reads around 2250us then we assume it as 1. Then we convert it in hex.
The incoming signal from remote contains 34 bits. We store all the bytes in the array and then decode the last byte to use.
while(ir == 1);
INT0IE = 0;
while(ir == 0);
TMR0=0;
while(ir == 1);
i++;
dat[i]=TMR0;
if(dat[1] > 5000 && dat[1]<12000)
{
}
else
{
i=0;
INT0IE = 1;
}
if(i>=33)
{
GIE=0;
delay(50);
cmd=0;
for(j=26;j<34;j++)
{
if(dat[j]>1000 && dat[j]<2000)
cmd<<=1;
else if(dat[j]>3500 && dat[j]<4500)
{
cmd|=0x01;
cmd<<=1;
}
}
cmd>>=1;
The above piece of code receives and decodes the IR signal using timer interrupts and stores the corresponding HEX value in the variable cmd. Now we can compare this HEX value (cmd variable) with our predefined HEX values and toggle the relay as shown below
if(cmd == 0xAF)
{
relay1=~relay1;
rly1LED=~rly1LED;
}
else if(cmd == 0x27)
{
relay2=~relay2;
rly2LED=~rly2LED;
}
else if(cmd == 0x07)
{
relay3=~relay3;
rly3LED=~rly3LED;
}
else if(cmd == 0xCF)
{
relay4=~relay4;
rly4LED=~rly4LED;
}
else if(cmd == 0x5f)
{
speed++;
if(speed>5)
{
speed=5;
}
}
else if(cmd == 0x9f)
{
speed--;
if(speed<=0)
{
speed=0;
}
}
Now to know at which our fan is currently operating, we should use a 7-segment display. The following lines are used to instruct the pins of the 7-segment display.
if(speed == 5) // turned off 5x2= 10ms triger //speed 0
{
PORTA=0xC0; // display 0
RB6=1;
fanLED=0;
}
else if(speed == 4 ) // 8 ms trigger //speed 1
{
PORTA=0xfc; // displaying 1
RB6=1;
fanLED=1;
}
else if(speed == 3) // 6 ms trigger // speed 2
{
PORTA=0xE4; // displaying 2
RB6=0;
fanLED=1;
}
else if(speed == 2) // 4ms trigger // speed 3
{
PORTA=0xF0; // displaying 3
RB6=0;
fanLED=1;
}
else if(speed == 1) // 2ms trigger // speed 4
{
PORTA=0xD9; // displaying 4
RB6=0;
fanLED=1;
}
else if(speed == 0) // 0ms trigger // speed 5 full power
{
PORTA=0xD2; // displaying 5
RB6=0;
fanLED=1;
}
The below function is for external interrupt and time overflow. This function is responsible for detecting zero crossing and driving the Triac.
void interrupt isr()
{
if(INT0IF)
{
delay(speed);
tric=1;
for(int t=0;t<100;t++);
tric=0;
INT0IF=0;
}
if(TMR0IF) //Check if it is TMR0 Overflow ISR
{
TMR0IF=0;
}
}
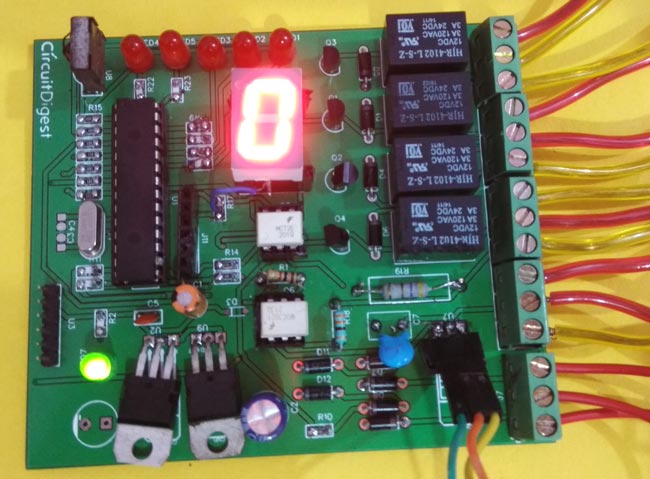
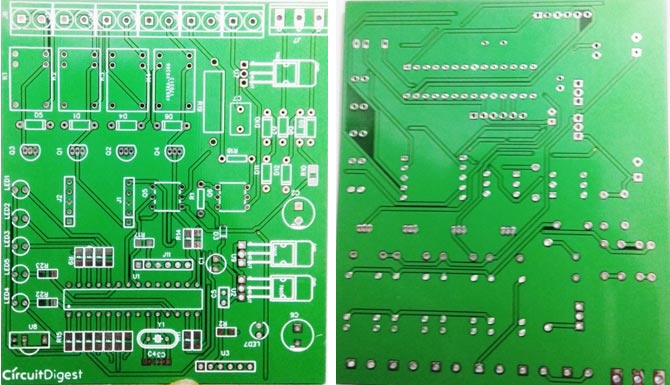
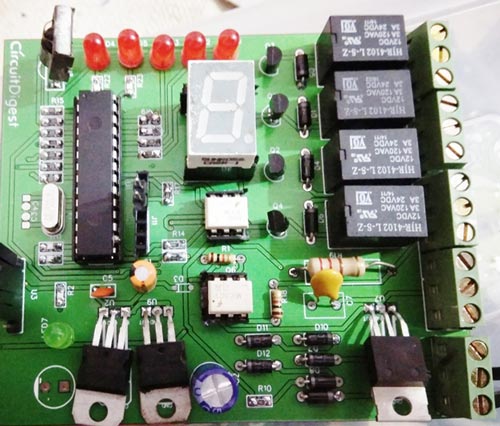
The final PCB for this IR remote controlled home automation looks as shown below:
Circuit and PCB Design using EasyEDA:
To design this
Remote control home automation we have used EasyEDA which is a free online EDA tool for creating circuits and PCBs in a seamless manner. We have previously ordered few
PCBs from EasyEDA and still using their services as we found the whole process, from drawing the circuits to ordering the PCBs, more convenient and efficient in comparison of other PCB fabricators. EasyEDA offers circuit drawing, simulation, PCB design for free and also offers high quality but low price Customized PCB service. Check here for the complete tutorial on
How to use Easy EDA for making Schematics, PCB layouts, Simulating the Circuits etc.
EasyEDA is improving day by day; they have added many new features and improved the overall user experience, which makes EasyEDA easier and usable for designing circuits. They are soon going to launch its Desktop version, which can be downloaded and installed on your computer for offline use.
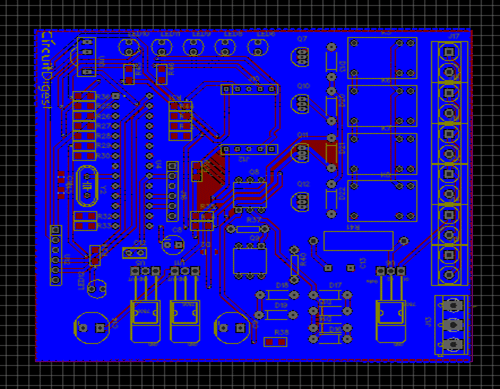
In EasyEDA, you can make your circuit and PCB designs public so that other users can copy or edit them and can take benefit from there, we have also made our whole Circuit and PCB layouts public for this
Remote control Home automation.
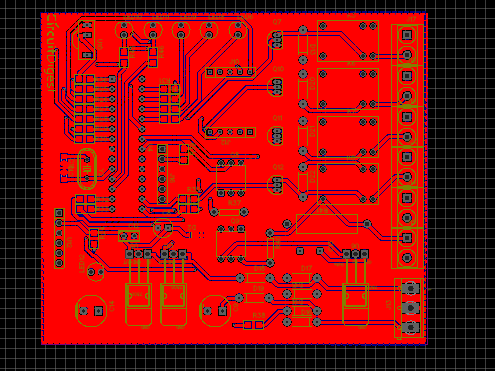
Below is the Snapshot of Top layer of PCB layout from EasyEDA, you can view any Layer (Top, Bottom, Topsilk, bottomsilk etc) of the PCB by selecting the layer form the ‘Layers’ Window.
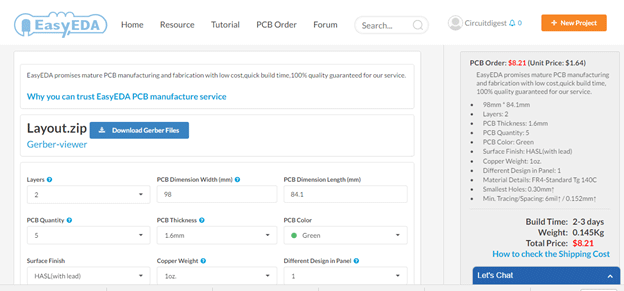
Calculating and Ordering PCB Samples online:
After completing the design of PCB, you can click the icon of
Fabrication output, which will take you on the
PCB order page. Here you can view your PCB in Gerber Viewer or download Gerber files of your PCB and send them to any manufacturer, it’s also a lot easier (and cheaper) to order it directly in EasyEDA. Here you can select the number of PCBs you want to order, how many copper layers you need, the PCB thickness, copper weight, and even the PCB color. After you have selected all of the options, click “Save to Cart” and complete your order, then you will receive your PCBs within few days.
You can directly order this PCB or download the Gerber file using
this link.
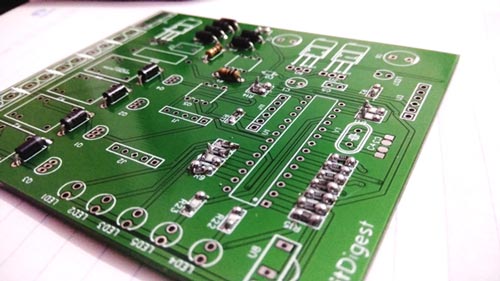
After few days of ordering PCB’s we got the PCBs. The boards that we received are shown below.
Once we received the PCBs I mounted all the required components over the PCB, and finally we have our IR Remote Controlled Home Automation ready, check this circuit working in demonstration video at the end of the article.